randomHAR: Improving Ensemble Deep Learners for Human Activity Recognition with Sensor Selection and Reinforcement Learning
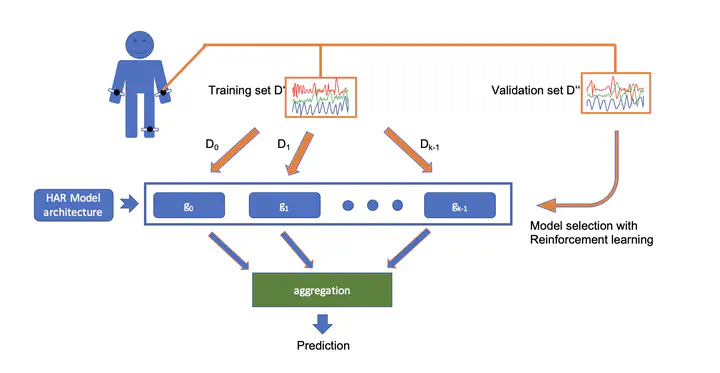 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
Deep learning has proven to be an effective approach in the field of Human activity recognition (HAR), outperforming other architectures that require manual feature engineering. Despite recent advancements, challenges inherent to HAR data, such as noisy data, intra-class variability and inter-class similarity, remain. To address these challenges, we propose an ensemble method, called randomHAR. The general idea behind randomHAR is training a series of deep learning models with the same architecture on randomly selected sensor data from the given dataset. Besides, an agent is trained with the reinforcement learning algorithm to identify the optimal subset of the trained models that are utilized for runtime prediction. In contrast to existing work, this approach optimizes the ensemble process rather than the architecture of the constituent models. To assess the performance of the approach, we compare it against two HAR algorithms, including the current state of the art, on six HAR benchmark datasets. The result of the experiment demonstrates that the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art method, ensembleLSTM.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.